By Shahab Khokhar
In the first part of this two-part blog series, we talked about how directional LiDAR help advance security applications, which you can read HERE.
In this second part, we discuss how directional LiDAR help reduce false alarms in security applications.
How Directional LiDAR Help Reduce False Alarms:
False alarms, an alarm that is set off needlessly, are a critical concern in any security application.
There are two major concerns about false alarms. First, action needs to be taken for each false alarm, which may include dispatching teams and equipment to the site, resulting in significant costs over time.
Second, if the false alarms persist, it causes “fatigue” in the response team as they are never sure if the alarm is false or true. This can result in lowering the efficiency of the response teams.
How false alarms are raised:
Camera-based systems are susceptible to false alarms due to many reasons, including but not limited to:
- Environmental factors
Cameras are quite vulnerable to fluctuations in environmental conditions, frequently leading to false alarms. Elements like wind, rain, and shadows can introduce movements or alterations in the visual scene that are mistakenly perceived as security threats. For instance, trees moving in the wind or the changing position of sunlight can cause camera systems to issue unnecessary alerts. This issue is especially prevalent in outdoor environments, where changes in the environment occur frequently.
- Sensitivity settings
Another significant factor contributing to false alarms is the sensitivity settings of camera systems. Many cameras have adjustable sensitivity levels, which help in detecting motion. However, if these settings are too high, even the smallest movement—such as a passing insect or falling leaf—can trigger an alert. Conversely, setting the sensitivity too low might cause the system to miss genuine threats. Striking the right balance is crucial but often challenging, leading to numerous false alerts in the process.
- Visual limitations
Cameras depend on visual information and are therefore influenced by lighting conditions. Poor lighting, excessive brightness, or glare can hinder the camera’s capacity to accurately record and analyze scenes. In dark or dimly lit environments, cameras may find it challenging to distinguish between harmless actions and potential dangers. This ambiguity can result in false alarms, where everyday movements are mistakenly identified as suspicious.
- Limited perspective
While cameras provide a visual record, they often lack depth perception, which is vital for understanding the context of movement and positioning of objects. A two-dimensional view can make it difficult to assess whether a detected movement is occurring within a secure perimeter or in an adjacent, unrelated area. This limitation often results in false alarms, as the camera cannot accurately judge the spatial relevance of detected motion.
- Wildlife and non-human activity
In areas where wildlife is present, or in urban environments with significant non-human activity, cameras frequently produce false alarms. Animals such as birds or pets moving in and out of the frame can trigger motion detection systems. Similarly, objects moved by wind or vehicles inadvertently entering the field of view are common causes of false alarms.
How Seyond’s Directional LiDAR helps reduce false alarms:
Seyond Directional LiDAR built upon the inherent advantages of 3D LiDAR and further reduce false alarms.
Denser point cloud:
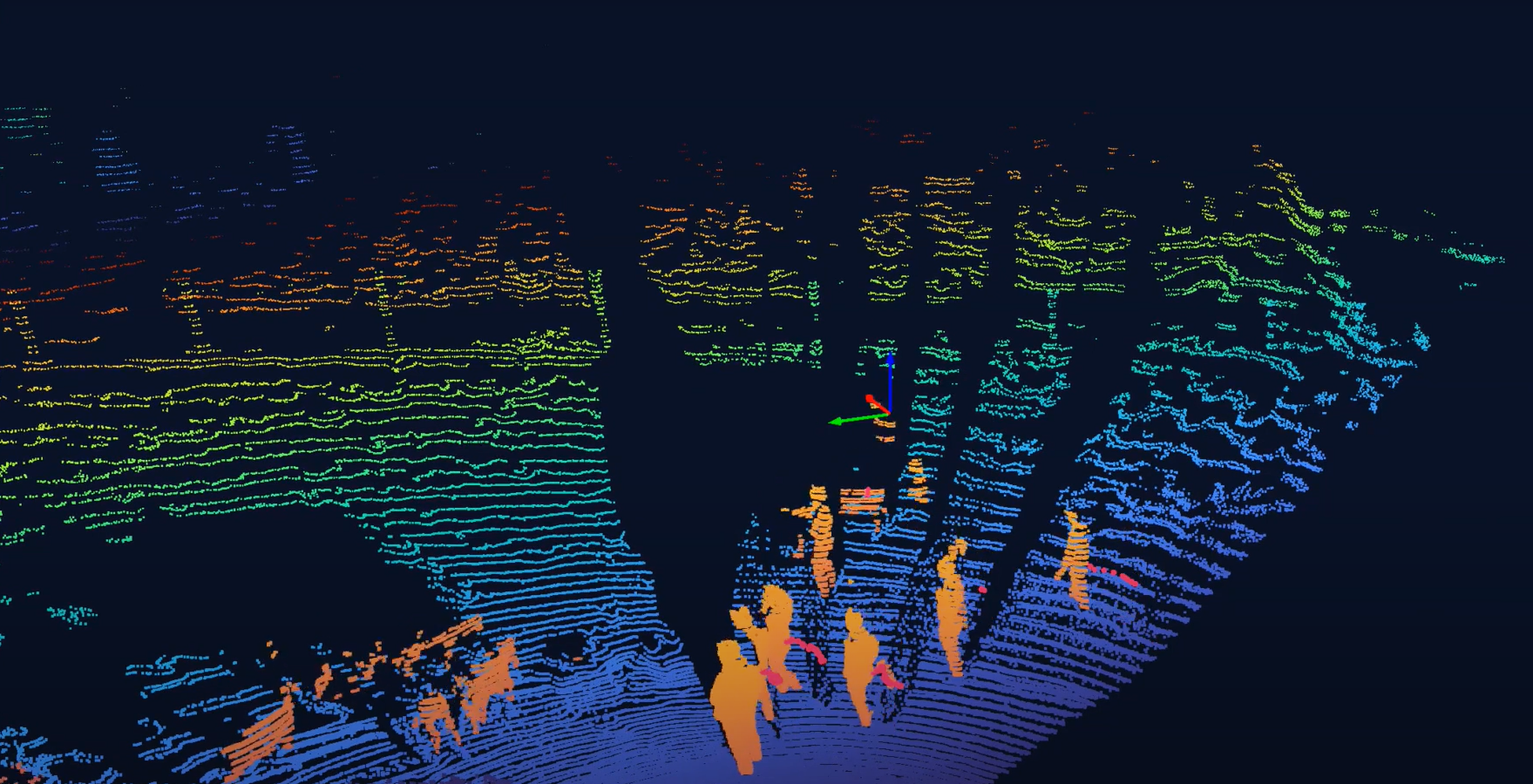
Seyond’s directional LiDAR, including the Falcon K, Robin W, and Robin E1X, feature ultra-high resolution, ensuring precision in detection. This level of precision is vital in security environments, where the ability to identify and differentiate between objects is critical.
Seyond directional LiDAR can accurately differentiate between objects based on size, shape, and movement patterns. This capability reduces the number of false alarms caused by non-threatening movements, such as animals or wind-blown debris.
With fewer false alarms, Seyond LiDAR systems streamline security operations and allow personnel to concentrate on genuine alerts, improving efficiency and response times.
Conversely, rotational LiDAR systems scan their laser beams across a broad field of view, which can reduce both resolution and depth perception, making it more difficult to clearly identify specific threats or intruders.
Focus on the danger:
Rotational 3D LiDAR spin 360 degrees. Most, if not all, security applications have specified areas of interest that need to be closely monitored. A 360-degree monitoring is very seldom required. Directional LiDAR excels at this. There is no rotation in directional LiDAR, and the beams point on the area of interest.
Seyond’s directional Falcon LiDAR offers a region of interest (ROI) dynamic focusing feature, which flexibly adjusts the region of interest for better target tracking. Even in challenging environmental conditions, it achieves enhanced clarity and higher safety levels.
Concealed installation:
Security LiDAR should not be easily visible. It is hard to do this with a rotating LiDAR as it needs to be installed in the middle of the protected space to make full use of the 360-degree view. Seyond directional LiDAR’s streamlined, compact design allows for a more concealed and unobtrusive installation. The LiDAR is not only less exposed but also more aesthetically pleasing.
Interference, processing and delay:
Rotational LiDAR is designed for scanning the entire 360-degree environment. If the LiDAR is attached to a wall or any other object, most of the 360-degree field of view is not needed thus reducing the effective duty cycle of point cloud scans. Seyond’s directional LiDAR scan the required areas only. The point cloud field of view they produce matches the security need and the data can be processed more efficiently.
Power consumption and reliability
Because rotational LiDAR contains relatively heavier components on the rotational stage many moving parts and are not designed and validated according to automotive LiDAR’s rigorous testing process due to its relatively lower production volume, they are more prone to malfunctioning and required regular maintenance and replacement. Seyond’s directional LiDAR, with a semi-solid-state structure and minimal moving parts, lasts longer and have lower maintenance needs. This is critical for security applications where replacement or maintenance can be costly due to the challenges in accessing the LiDAR installation and the disruption in operations during maintenance.
Seyond’s mass-produced directional LiDAR, Falcon K, represents Seyond’s dedication to excellence. It has successfully passed a series of standard reliability tests including tests for resistance to harmful gases, chemical corrosion, temperature and humidity variations, frost, thermal cycles, and impact resilience. Even in the most demanding environments, it delivers unwavering performance stability. With over 400,000 units already delivered, Falcon K is a testament to our commitment to quality and reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Seyond’s directional LiDAR systems can provide improved accuracy, real-time processing, reduced power consumption, and greater versatility for security applications. Their capability to accurately track and differentiate between objects in a 3-dimensional designated region makes them a preferred option compared to rotational LiDAR, particularly in sensitive and complex environments that require a high level of security with very low false alarms. As the need for effective security solutions increases, the use of Seyond’s directional LiDAR technology is expected to grow, offering enhanced safety and reassurance across various security applications.